|
1. Which of the following is the definition of a pair of diastereomers?
(A) A pair of structures that are superimposable mirror images of one another
(B) A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another
(C) A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another
(D) A pair of stereoisomers that have equal specific rotations
2. Which of the following statements is not true regarding pairs of enantiomers?
(A) They have identical melting points
(B) They have identical boiling points
(C) They rotate plane polarized light in opposite directions
(D) They react at identical rates with chiral reagents
3. Which of the following structures is different from the other three?
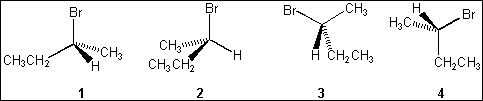
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
4. Which of the following compounds is/are chiral?

(A) only 1
(B) only 1 and 2
(C) only 2 and 3
(D) 1, 2 and 3
5.Which of the following have the R configuration ?
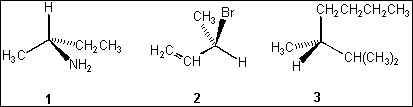 (A) only 1
(B) only 2
(C) only 1 and 2
(D) 1, 2 and 3
6. Which of the following Newman projections represents (2R,3R)-dibromobutane?
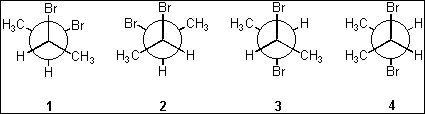 (A)
1
(B)
2
(C)
3
(D)
4
7. Which of the following structures represent the same stereoisomer?
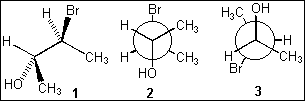
(A) only 1 and 2
(B) only 1 and 3
(C) only 2 and 3
(D) 1, 2 and 3
8. How many stereoisomers of
3-bromo-2-butanol, CH3CH(OH)CHBrCH3, exist?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
9. How much of the R enantiomer is present in 10 g of a mixture which has an enantiomeric excess of 20% of the S isomer?
(A) 1 g
(B) 2 g
(C) 4 g
(D) 6 g
10. A solution of 0.1 g/mL of a pure R enantiomer in a 1 dm polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +4.8°. What is the rotation observed on this solution in a 2 dm polarimeter?
(A) +2.4°
(B) +4.8°
(C) +9.6°
(D) +24°
|