|
1. The reaction of tert-butyl
bromide, (CH3)3CBr, with methanol in an inert solvent
proceeds by an SN1 mechanism to give tert-butyl methyl ether,
(CH3)3COCH3. What is the effect of doubling the
concentration of methanol on the rate of the reaction?
(A) the rate remains the same
(B) the rate decreases by a factor of 2
(C) the rate increases by a factor of 2
(D) the rate increases by a factor of 4
2. Which of the following
alkyl halides undergoes the fastest SN2 reaction with sodium
methylthiolate, NaSMe?
(A) methyl iodide
(B) ethyl iodide
(C) 2-bromopropane
(D) tert-butyl chloride
3. Which of the following
alkyl halides undergoes the fastest solvolysis reaction with ethanol, CH3CH2OH?
(A) methyl fluoride
(B) ethyl bromide
(C) 2-chloropropane
(D) tert-butyl bromide
4. What is the major organic
product obtained from the following reaction?
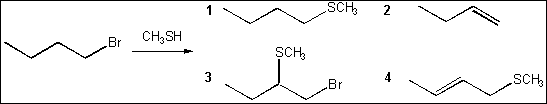
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
5. Which of the following
anions is the most nucleophilic in polar protic solvents??
(A) F-
(B) Cl-
(C) Br-
(D) I-
6. Which of the following is
the most nucleophilic?
(A) sodium ethoxide
(B) acetic acid
(C) methanol
(D) water
7. What is the major organic
product obtained from the following reaction?
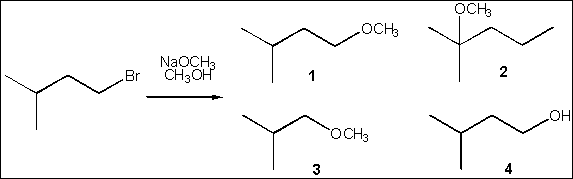
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
8. Which of the following represents the transition state of the SN2 reaction between methyl
iodide and ammonia?
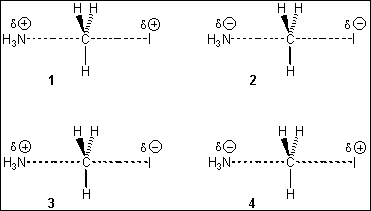
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
9. Which of the
following is not a characteristic of SN1
reactions?
(A) the electrophilic carbon undergoes inversion of stereochemistry
(B)
the rate is proportional to the concentration of substrate
(C) the reaction proceeds faster in a more polar solvent
(D) the rate is independent of the concentration of nucleophile
10. Which of the following
represents the transition state of the rate-determining step in the SN1
reaction between tert-butyl chloride and water?
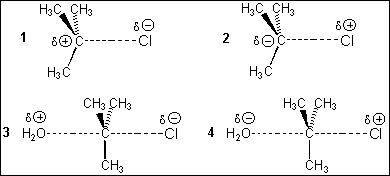 (A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
|