|
1. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
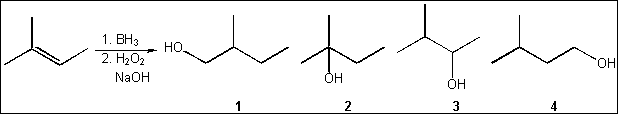
(A)
1 (B)
2
(C)
3
(D)
4
2. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
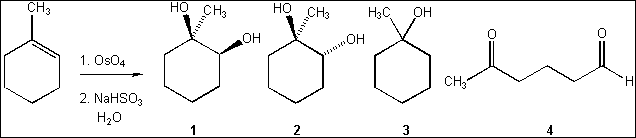
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
3. What is (are) the major organic product(s) obtained from the following reaction?
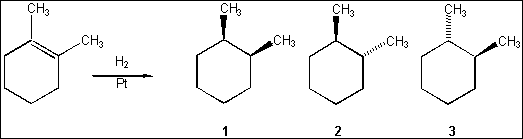
(A)
only 1
(B)
only 2
(C)
only 3
(D)
only 2 and 3
4. What is (are) the major organic product(s) obtained from the following
reaction?
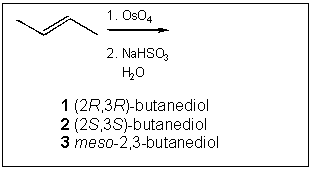
(A) only
1
(B) only
2
(C) only
3
(D) only
1 and 2
5. What is the best choice of reagent(s) to perform the following transformation?
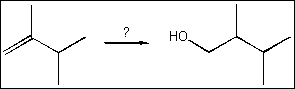
(A) H2O, H2SO4
(B) Hg(OAc)2
and H2O ; followed by NaBH4
(C) B2H6;
followed by H2O2, NaOH
(D) OsO4;
followed by NaHSO3
6. What type of reaction
mechanism accounts for the reaction of an alkene with aqueous acid to give an
alcohol?
(A) nucleophilic addition
(B) electrophilic addition
(C) radical addition
(D) elimination
7. What is the correct order of exothermicity for hydrogenation of the following butenes
upon treatment with H2/Pd (more exothermic > less exothermic)?
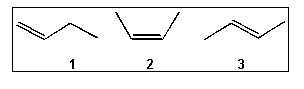
(A) 1 > 2 > 3
(B) 3 > 2 > 1
(C) 1 > 3 > 2
(D) 2 > 3 > 1
8. Which of the following reactions of alkenes is stereospecific?
(A) addition of HCl (treatment with HCl)
(B) hydrogenation (treatment with H2/Pt)
(C) addition of HBr (treatment with HBr)
(D) acid-catalyzed hydration (treatment with aqueous H2SO4)
9. Which of the following concepts explains why tertiary carbocations are more stable than primary and secondary carbocations?
(A) electronegativity
(B) resonance
(C) hyperconjugation
(D)
Aufbau principle
10. What is the best choice of reagent(s) to perform the following transformation?
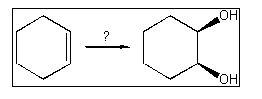
(A) H2O, H2SO4
(B) HgSO4;
followed by NaBH4
(C) BH3;
followed by H2O2
(D) OsO4;
followed by NaHSO3
|